Tripartite interactions between filamentous Pf4 bacteriophage, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and bacterivorous nematodes
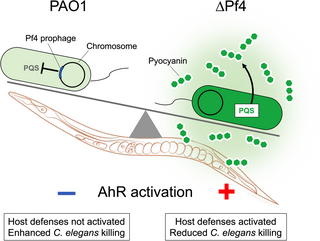
"Collectively, our data support a model where suppression of quorum-regulated virulence factors by Pf4 allows P. aeruginosa to evade detection by innate host immune responses."
journals.plos.org/plospathogen…
#viruses #virology #symbiosis #phage
Tripartite interactions between filamentous Pf4 bacteriophage, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and bacterivorous nematodes
Author summary Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic bacterial pathogen that infects wounds, lungs, and medical hardware. P. aeruginosa strains are often themselves infected by a filamentous virus (phage) called Pf.journals.plos.org