Search
Items tagged with: symbiosis
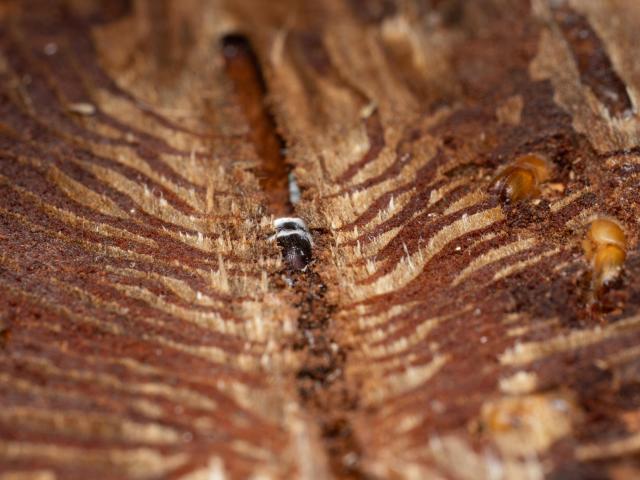
#Fungi disarm #BarkBeetle chemical shields by converting their plant-derived toxins phys.org/news/2025-12-fungus-b… pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2525…
"a bark beetle can co-opt a tree's defensive compounds to make defenses against its own enemies. However, since one of the enemies, the #fungus Beauveria bassiana, has developed the ability to detoxify these antimicrobial defenses, it can successfully infect the #BarkBeetles and thus actually help the tree in its battle against bark #beetles"
Fungus disarms bark beetle chemical shields by converting their plant-derived toxins
Spruce bark is rich in phenolic compounds that protect trees from pathogenic fungi. A research team at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena has investigated how these plant defenses function within the food web, particularly in spruc…Max Planck Society (Phys.org)
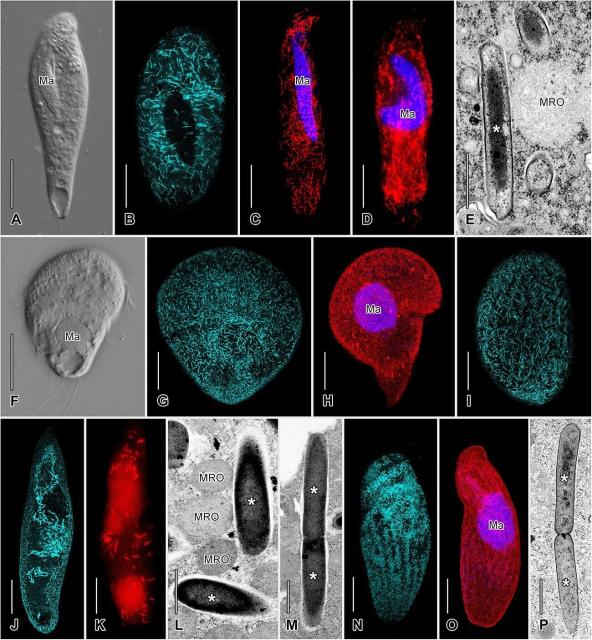
Advanced genetic techniques and #microscopy offer new insights into anaerobic ciliate and methanogen #symbiosis phys.org/news/2024-10-advanced…
Methanogenic #symbionts of anaerobic #ciliates are host and habitat specific academic.oup.com/ismej/article… #ISEPpapers by @joro
"This study provides a clearer understanding of how anaerobic ciliates have evolved a mix transmission mode to both maintain and replace their symbionts over time"
#microbes #protists #bacteria #archaea #methanogenesis #biology
Advanced genetic techniques and microscopy offer new insights into anaerobic ciliate and methanogen symbiosis
A recent study has uncovered critical details about the association between anaerobic ciliates and methanogenic archaea, a relationship that has fascinated scientists for over decades.Charles University (Phys.org)
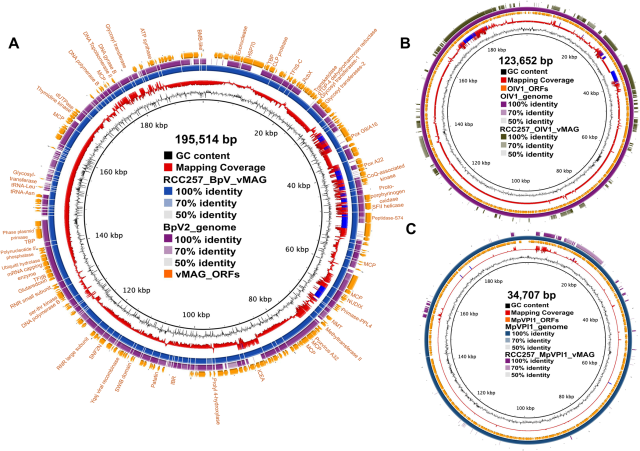
Genetic potential for aerobic respiration and denitrification in globally distributed respiratory endosymbionts
nature.com/articles/s41467-024…
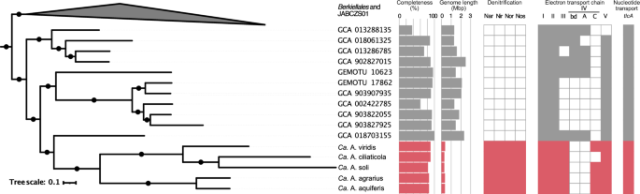
Genetic potential for aerobic respiration and denitrification in globally distributed respiratory endosymbionts - Nature Communications
In this study, the authors report and analyze four complete genomes of respiratory endosymbionts to show that they carry the potential to breathe both oxygen and nitrogen oxides providing energy to their hosts.Nature
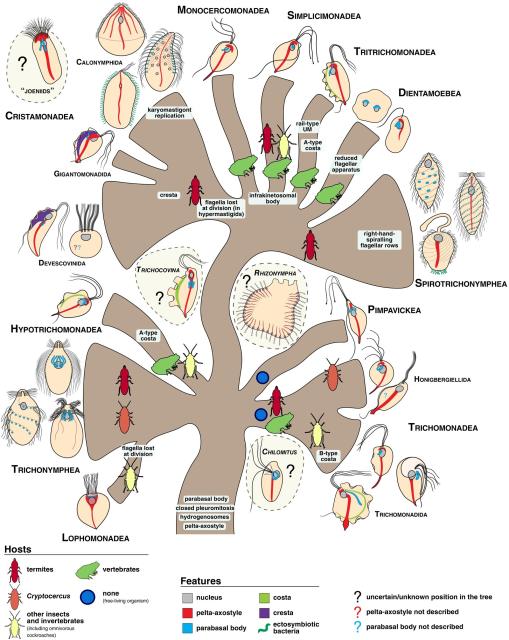
New #ISEPpapers! Updated classification of the phylum Parabasalia onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/fu…
"Most are harmless or beneficial gut #symbionts of #animals, but some have turned into #parasites in other body compartments, the most notorious example being #Trichomonas vaginalis in humans."
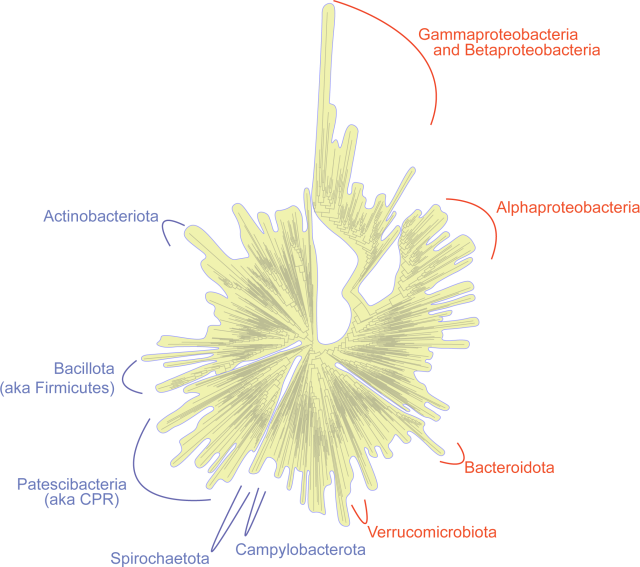
Genomic analyses of Symbiomonas scintillans show no evidence for endosymbiotic bacteria but does reveal the presence of giant viruses
Author summary Endosymbiotic bacteria are found in a wide variety of hosts across the tree of eukaryotes and have been proposed to be evolutionarily and ecologically significant, but in most cases, we know little to nothing about them.journals.plos.org
Distinct life cycle stages of an ectosymbiotic DPANN archaeon
academic.oup.com/ismej/article…
#archaea #symbiosis #microbiology

Distinct life cycle stages of an ectosymbiotic DPANN archaeon
Abstract. DPANN archaea are a diverse group of microorganisms that are thought to rely on an ectosymbiotic lifestyle; however, the cell biology of these ceGaisin, Vasil A (Oxford University Press)
The move from a free-living environment to an endosymbiotic relationship has profound effects on bacterial function.
This #PLOSBiology Unsolved Mystery from John P McCutcheon &co explores how bacterial endosymbionts work with so few genes. #symbiosis
How do bacterial endosymbionts work with so few genes?
The move from a free-living environment to a long-term residence inside a host eukaryotic cell has profound effects on bacterial function.plos.io
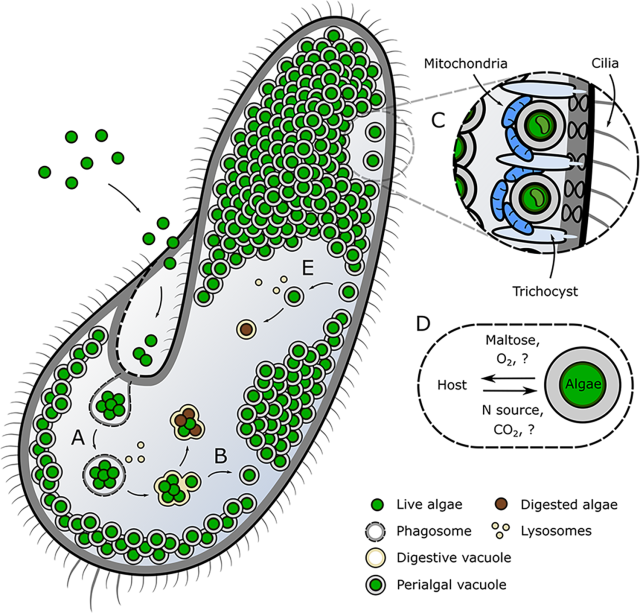
#Mutualism on the edge: Understanding the #Paramecium–#Chlorella symbiosis journals.plos.org/plosbiology/…
"Exploring the mechanisms that underpin #symbiosis requires an understanding of how these complex interactions are maintained in diverse model systems. The ciliate #protist, Paramecium bursaria, offers a valuable insight into how emergent endosymbiotic interactions have evolved."
#protists #algae #microbes #ciliates
Mutualism on the edge: Understanding the Paramecium–Chlorella symbiosis
Exploring the mechanisms that underpin symbiosis requires an understanding of how these complex interactions are maintained in diverse model systems.journals.plos.org
Beyond pathogenesis: Detecting the full spectrum of ecological interactions in the virosphere
"Viral interactions with their hosts are complex and some non-pathogenic viruses could have potential benefits to society. However, viral research is seldom designed to identify viral mutualists, a gap that merits considering new experimental designs."
journals.plos.org/plosbiology/…
#viruses #pathogens #symbiosis
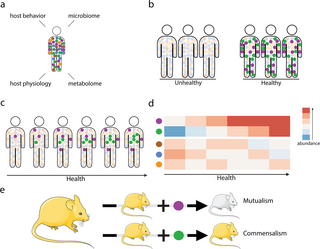
Beyond pathogenesis: Detecting the full spectrum of ecological interactions in the virosphere
Viral interactions with their hosts are complex and can be beneficial, yet the public perception of viruses is generally negative.journals.plos.org
#photosymbiosis #symbiosis #purplebacteria #ciliates #pseudoblepharisma #anaerobcieuks
Gotta love the term "threshold of lichenisation" - sounds dramatic. Cool study!
Alcobiosis, an algal-fungal association on the threshold of lichenisation
nature.com/articles/s41598-023…
#symbiosis #lichen #algae #fungi
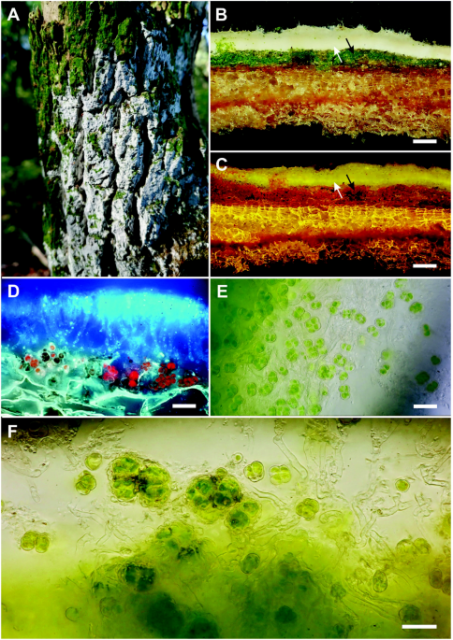
Alcobiosis, an algal-fungal association on the threshold of lichenisation - Scientific Reports
Scientific Reports - Alcobiosis, an algal-fungal association on the threshold of lichenisationNature
Conifer-killing bark beetles locate fungal symbionts by detecting volatile fungal metabolites of host tree resin monoterpenes
journals.plos.org/plosbiology/…
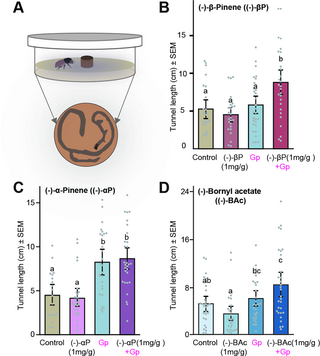
Conifer-killing bark beetles locate fungal symbionts by detecting volatile fungal metabolites of host tree resin monoterpenes
Outbreaks of the Eurasian spruce bark beetle have decimated millions of hectares of conifer forests in Europe in recent years.journals.plos.org
Tripartite interactions between filamentous Pf4 bacteriophage, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and bacterivorous nematodes
"Collectively, our data support a model where suppression of quorum-regulated virulence factors by Pf4 allows P. aeruginosa to evade detection by innate host immune responses."
journals.plos.org/plospathogen…
#viruses #virology #symbiosis #phage
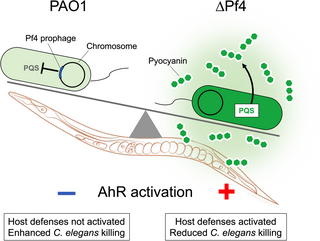
Tripartite interactions between filamentous Pf4 bacteriophage, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and bacterivorous nematodes
Author summary Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic bacterial pathogen that infects wounds, lungs, and medical hardware. P. aeruginosa strains are often themselves infected by a filamentous virus (phage) called Pf.journals.plos.org
Fascinating study examining the switch from coexistence to pathogenicity in a marine association
Bacterial lifestyle switch in response to algal metabolites
elifesciences.org/articles/844…
#microbiology #marine #symbiosis

Bacterial lifestyle switch in response to algal metabolites
Opportunistic bacteria modulate their lifestyle from coexistence to pathogenicity by perceiving the physiological state of their algal host through sensing of algal secreted metabolites.Noa Barak-Gavish (eLife Sciences Publications, Ltd)
@jobsecoevo #ScienceJobs #PostdocJob #EcoEvo #CellBiology #Genetics #Symbiosis #Bacteria #Insects #Wolbachia #Drosophila
Postdoctoral Scholar of Host-Microbe Interactions
The Shropshire Lab (Lehigh University, Pennsylvania) is seeking a highly motivated Postdoctoral researcher to study host-microbe interactions.https://shropshirelab.com/author/j-dylan-shropshireprotonmail-com/#author (My WordPress)