Search
Items tagged with: phytoplankton
With spring 🌱 upon us in the northern hemisphere, it is the time for the spring bloom in many lakes and oceans. To grow, #phytoplankton require #nutrients and #light, so start reproducing rapidly due to an abundance of nutrients mixed in the water column and increased light intensity 🌞. Zooplankton grazers have yet to increase, and warming conditions help to retain algae near the surface euphotic zone via stratification.
serc.carleton.edu/eet/phytopla…
#Science #climate
#Plankton mark #seasons in the #sea, just like leaves and flowers on land.
theconversation.com/plankton-m…
Plankton mark seasons in the sea, just like leaves and flowers on land
Plankton bloom and wither with the seasons much as plants do on land.The Conversation
Over the past few weeks, a #phytoplankton #bloom has been observed in the northern Adriatic Sea.
High temperatures and freshwater inputs from recent heavy rainfall have favoured the bloom.
The freshwater input has reduced the sea surface salinity, creating an ideal environment for the rapid proliferation of phytoplankton.
Rising temperatures have further accelerated the process, making the bloom so large that it is even visible from space.
The bloom has also led to the formation of #mucilage, which has accumulated along the coasts of some Italian regions bordering the Adriatic Sea.
This image, acquired by one of the Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellites on 7 August 2024,
shows both the mucilage (in white) and the phytoplankton bloom (in green) off the coast of the city of Rimini.
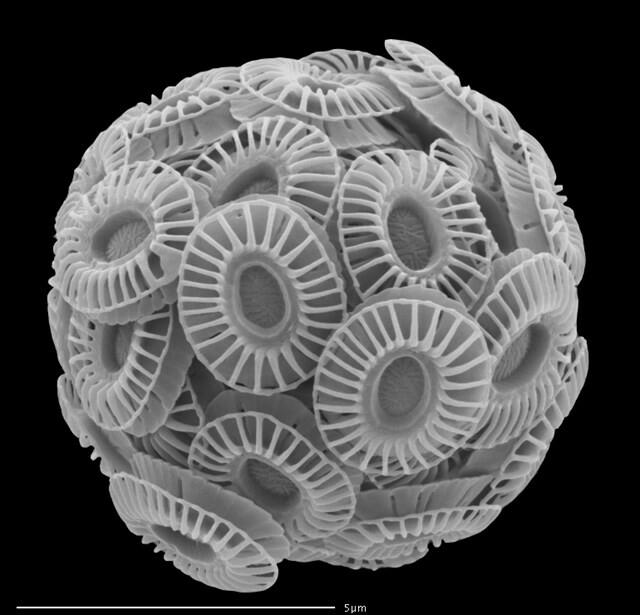
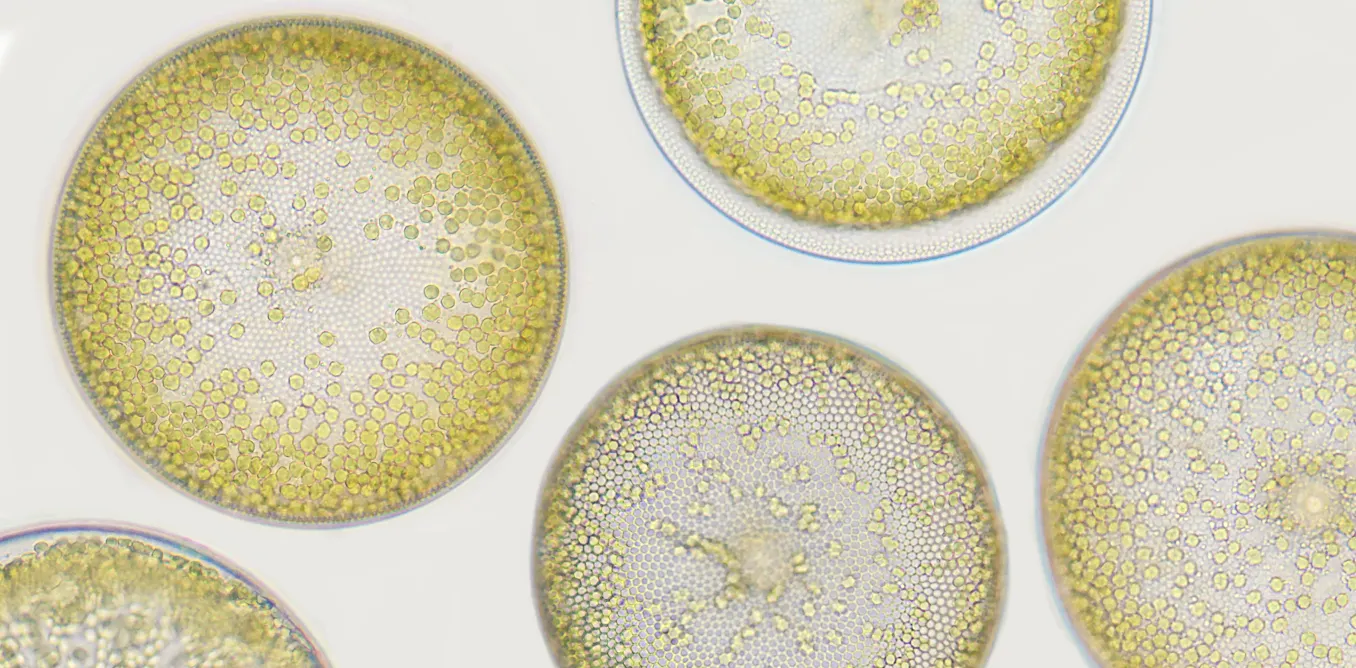
Coccolithophores (phylum Haptista) are a type of #phytoplankton covered in white calcium carbonate coccolith plates. Blooms in the surface seas can be seen in satellite images because these shells. They are the primary component in #chalk deposits such as the white cliffs of Dover (the "calcite belt" in the temperate north) and as such are very important for the biological carbon pump.
#climate
Emiliania huxleyi (below) is a common species.
joidesresolution.org/the-magic…
The Magical World of Coccolithophores
What are these beautiful algae? Where are they found and why are they important? Teachers down load the word document at the end of the article with questions. These photographs show 4 coccolitho…JOIDES Resolution
#Virus control
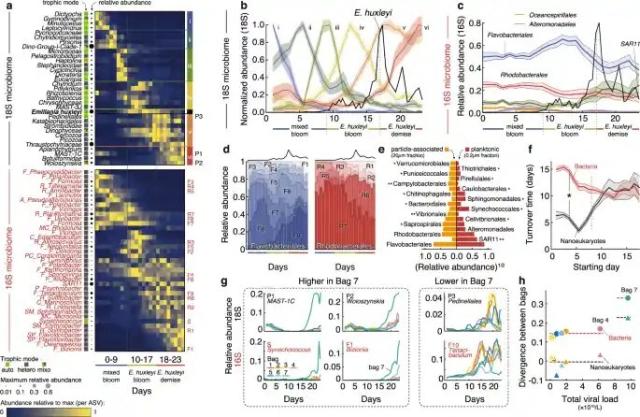
This exciting new research explores the influence of #virus #infection in changing the balance of organic matter degradation between #bacteria and #eukaryotes in #marine #carboncycling during #phytoplankton blooms.
Based on #mesocosm studies, this research demonstrates how #viruses infecting different #microorganisms change community dynamics and the release and potential fate of marine carbon from primary production.
Learn more in this new research in Nature Communications on:
nature.com/articles/s41467-023…
#microbiology #ecology #MicrobialEcology
Viral infection switches the balance between bacterial and eukaryotic recyclers of organic matter during coccolithophore blooms - Nature Communications
Algal blooms are hotspots of marine primary production that play central roles in microbial ecology and global elemental cycling.Nature
This is interesting and might be relevant for bloom-ending processes in #phytoplankton. Roseobacter can coexist with Emiliania huxleyi (and important bloom forming coccolithophore important to carbon cycling), providing vitamins for ready supplies of sugar and amino acids. However when an algal cell is dying they bacteria can collect additional compounds and leave in search other other hosts. #algae #oceanography
phys.org/news/2023-01-friend-f…
'Friend or foe' bacteria kill their algal hosts when coexisting is no longer beneficial
Scientists have detailed a lifestyle switch that occurs in marine bacteria, in which they change from coexisting with algae hosts in a mutually beneficial interaction to suddenly killing them. The results are published today in eLife.Science X (Phys.org)