Search
Items tagged with: biorxiv
New #ISEPpapers #preprint! Comprehensive analysis of the microbial consortium in the culture of flagellate #Monocercomonoides exilis biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20… #protists #microbes #mitochondria #bacteria #biorxiv @biorxivpreprint
"Monocercomonoides exilis is the only known amitochondriate eukaryote, making it an excellent model for studying the implications of mitochondrial reduction from a cellular and evolutionary point of view."
Comprehensive analysis of the microbial consortium in the culture of flagellate Monocercomonoides exilis
Monocercomonoides exilis is the only known amitochondriate eukaryote, making it an excellent model for studying the implications of mitochondrial reduction from a cellular and evolutionary point of view. Although M.bioRxiv

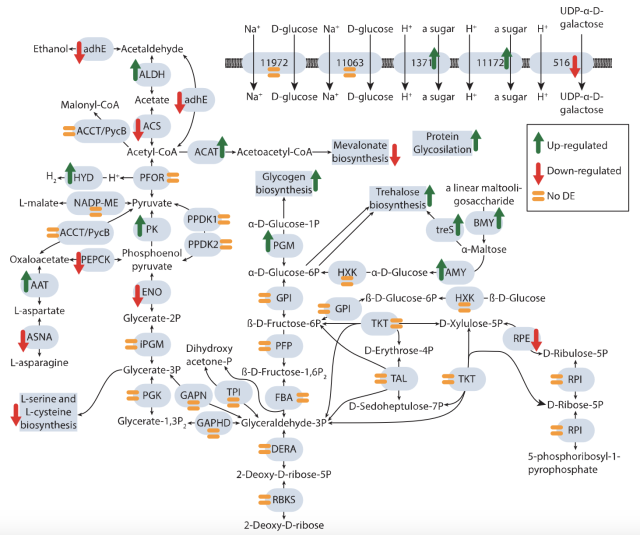
A patchwork pathway of apparently recent origin enables degradation of the synthetic buffer compound TRIS in bacteria
The widely used synthetic chemical 2-amino-2-hydroxymethyl-propane-1,3-diol (TRIS) was long considered to be biologically inert. Herein, we describe a complete degradation pathway for the catabolism of TRIS in bacteria.bioRxiv
Phages... So many #phage and they are all #prophage integrated into a #bacteria #genome
A few million prophages from > million bacterial genomes
Are prophages good or bad for bacteria? The data shows they provide heaps of benefits
The paper is in #biorxiv and the data is on #figshare
biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20…
open.flinders.edu.au/projects/…

The Promise and Pitfalls of Prophages
Phages dominate every ecosystem on the planet. While virulent phages sculpt the microbiome by killing their bacterial hosts, temperate phages provide unique growth advantages to their hosts through lysogenic conversion.bioRxiv