Search
Items tagged with: preprint
New #ISEPpapers #preprint! Viral infection to the raphidophycean alga #Heterosigma akashiwo affects both intracellular organic matter composition and dynamics of a coastal prokaryotic community biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20…
#protists #algae #viruses #microbes #biology
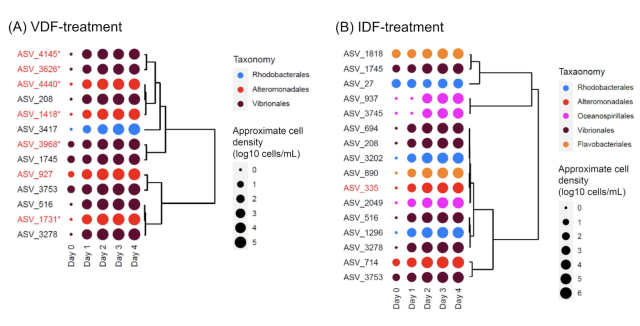
Viral infection to the raphidophycean alga Heterosigma akashiwo affects both intracellular organic matter composition and dynamics of a coastal prokaryotic community
Marine microalgae play a crucial role in marine ecosystem by supplying dissolved organic matter to heterotrophic prokaryotes, which mediate the microbial loop.bioRxiv
New #ISEPpapers #preprint! Comprehensive analysis of the microbial consortium in the culture of flagellate #Monocercomonoides exilis biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20… #protists #microbes #mitochondria #bacteria #biorxiv @biorxivpreprint
"Monocercomonoides exilis is the only known amitochondriate eukaryote, making it an excellent model for studying the implications of mitochondrial reduction from a cellular and evolutionary point of view."
Comprehensive analysis of the microbial consortium in the culture of flagellate Monocercomonoides exilis
Monocercomonoides exilis is the only known amitochondriate eukaryote, making it an excellent model for studying the implications of mitochondrial reduction from a cellular and evolutionary point of view. Although M.bioRxiv
"Here, we engineered tobacco rattle virus to carry the compact RNA-guided TnpB enzyme ISYmu1 and its guide RNA. This innovation allowed transgene-free editing of #Arabidopsis thaliana in a single step, with edits inherited in the subsequent generation. "
#Preprint
biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20…

Viral delivery of an RNA-guided genome editor for transgene-free plant germline editing
Genome editing is transforming plant biology by enabling precise DNA modifications. However, delivery of editing systems into plants remains challenging, often requiring slow, genotype-specific methods such as tissue culture or transformation.bioRxiv
"Our two laboratories encountered independently sudden-onset, major impediments to such research. Spore suspensions and vegetative cells no longer plated effectively on minimal media. By systematically analyzing multiple different media components from multiple different suppliers, we identified the source of the problem"
biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20…

Laboratory horror stories: Poison in the agars
The fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe is a single-celled eukaryote that can be cultured as a haploid or as a diploid.bioRxiv
'Both genomes had been analysed before, but the fragmented assemblies had scaffold sizes comparable to the length of long reads prior to assembly. Our new assemblies illustrate how long-read technologies allow for a much better representation of species genomes. We are now able to conduct more accurate downstream assays based on more complete gene and transposable element predictions.'
#Preprint #Evolution #Genomics
biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20…

Revisiting genomes of non-model species with long reads yields new insights into their biology and evolution
High-quality genomes obtained using long-read data allow not only for a better understanding of heterozygosity levels, repeat content, and more accurate gene annotation, and prediction when compared to those obtained with short-read technologies, but…bioRxiv
Encyclopaedia of DNA polymerases localized in organelles: Evolutionary contribution of diverse bacteria including the proto-mitochondrion
DNA polymerases (DNAPs) synthesize DNA from deoxyribonucleotides in a semi-conservative manner and serve as the core of DNA replication and repair machineries.bioRxiv
New preprint on inter-plasmid competition via type IV-A3 CRISPR systems. Something to think about.
biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20…

Type IV-A3 CRISPR-Cas systems drive inter-plasmid conflicts by acquiring spacers in trans
Type IV-A CRISPR-Cas systems are primarily encoded on plasmids and form multi-subunit ribonucleoprotein complexes with unknown biological functions.bioRxiv
'To address this critical knowledge gap, we conducted a comprehensive cross-species analysis of transcriptomic data from over 6000 blood samples from macaques and humans infected with one of 31 viruses, including #Lassa, #Ebola, #Marburg, #Zika, and #dengue.'
#Immunology #Virology #preprint
biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20…

Systems immunology of transcriptional responses to viral infection identifies conserved antiviral pathways across macaques and humans
Viral pandemics and epidemics pose a significant global threat, with emerging and re-emerging viruses responsible for four pandemics in the 21st century alone.bioRxiv
#ScienceMastodon #RNA #mRNA #preprint #mpinat

Nuclear export is a limiting factor in eukaryotic mRNA metabolism
The eukaryotic mRNA life cycle includes transcription, nuclear mRNA export and degradation. To quantify all these processes simultaneously, we perform thiol-linked alkylation after metabolic labeling of RNA with 4-thiouridine (4sU), followed by seque…bioRxiv
An antibacterial peptide encoded in the mitochondrial genome (#preprint).
#immunology #InnateImmunity
"We demonstrate that MOTS-c (mitochondrial open reading frame from the twelve S rRNA type-c) is a mitochondrial-encoded amphipathic and cationic peptide with direct antibacterial and immunomodulatory functions, consistent with the peptide chemistry and functions of known HDPs."
biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20…

The Human Mitochondrial Genome Encodes for an Interferon-Responsive Host Defense Peptide
The mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) can trigger immune responses and directly entrap pathogens, but it is not known to encode for active immune factors. The immune system is traditionally thought to be exclusively nuclear-encoded.bioRxiv
(I realize that some of these suggestions would best be used simulatenously, e.g., #newPaper and #preprint have obviously different content. What I am searching for is a common tag for *threads* explaining research articles, not only posts announcing a new publication 🙂.
I had to drop one tag bc of the 5-option limit in polls, and I went for #mastoPrint as it was my own suggestion.)
Some further thoughts:
One could combine these tags in a standardized way with research field names, e.g. #newNeuroPaper, #neuroPreprint, or #neuroPaperThread.
Also, please remember to use #camelCase or #CamelCase notation in these tags for screenreader accessibility!
Tagging some people who responded to my first post (sorry for bothering you!):
@mwt @toddhorowitz @achterbrain @PessoaBrain @elduvelle @Brendanjones @gdiak @EricLawton @annettamallon @UlrikeHahn @ryneches @x1l3f @nyates314 @bsweber @ArneBab @tfardet @emergentnexus @DrAnneCarpenter @f @harcel @MarkHanson @Iris
Hi #science #research #mastodon community! A few days ago, a post of mine recieved a lot of attention. Thanks for the engagement and the very interesting suggestions! neuromatch.social/@LeonDLotter…
On #Twitter, I loved the common practice of writing threads explaining new #preprints and #papers in an understandable way.
I uttered my concern that through the chronological timeline here people might miss interesting science. A solution would be to agree on names for hashtags and/or a.gup.pe groups to ease tracking these "paper threads".
Following tags were named more then once: #newPaper #paperThread #preprint #researchPaper #mastoPrint #tootPrint.
Also, there was #tootorial, but that might be a slightly different category?
I heard people like participation - so let's do a poll! What's your favourite tag for threads explaining research articles? 📊 Multiple choices possible!
#twitterMigration #scienceTwitter #scientist @academicchatter @neuroscience @cognition @psychology @phdstudents

Leon Lotter (@LeonDLotter@neuromatch.social)
On #scienceTwitter, my favourite thing was reading and, on rare occasions, writing "paper/preprint threads". From the researchers I followed and through the #Twitter algorithm, this became my most important source for new #research.Neuromatch Social
- #newPaper (26%, 67 votes)
- #paperThread (37%, 93 votes)
- #preprint (27%, 68 votes)
- #researchPaper (34%, 85 votes)
- #tootPrint (9%, 23 votes)
Evidence for a core set of microbial lichen symbionts from a global survey of metagenomes
Lichens are the archetypal symbiosis and the one for which the term was coined. Although application of shotgun sequencing techniques has shown that many lichen symbioses can harbour more symbionts than the canonically recognized fungus and photobion…bioRxiv

Assessing the biogeography of marine giant viruses in four oceanic transects
Viruses of the phylum Nucleocytoviricota are ubiquitous in ocean waters and play important roles in shaping the dynamics of marine ecosystems.bioRxiv
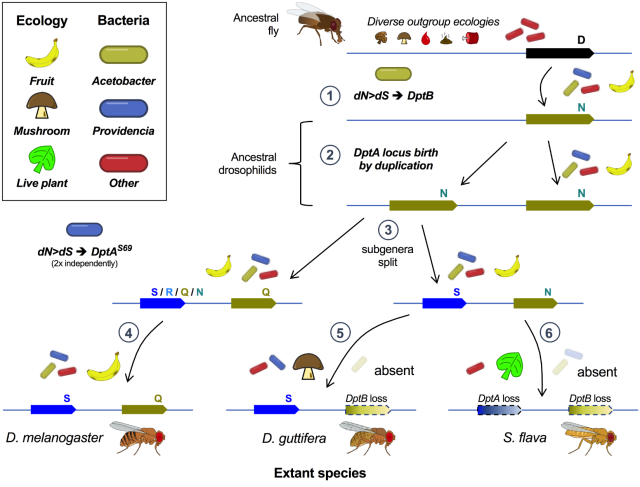
Happy to announce this #preprint , the culmination of last 10 years. 🥳
We find that #antimicrobialpeptides are evolved to control specific #microbiome #bacteria. This example is a textbook case of host #immune #evolution being shaped by the microbiome 🦠 which depends on host #ecology.
Thanks for comments! Bit of an experiment: we are posting pre-submit to get feedback 🙂.
biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/20…
#immunity #Drosophila #EvolutionaryBiology #inflammation #NFkB
Single innate immune effectors control ecological microbiome bacteria across evolutionary timescales
Antimicrobial peptides are host-encoded antibiotics that combat invading microbes and help shape the microbiome in plants and animals.bioRxiv
Stumbled upon @drewendy making me remember this gem of a #preprint It provoked me to think about how dual-use research of concern can be used oppressively. And challenges me to think about #synbio research that is also #frugalInnovation

Complete absence of thebaine biosynthesis under home-brew fermentation conditions
Yeast-based biosynthesis of medicinal compounds traditionally derived from plant materials is improving.bioRxiv